Git 是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,用于敏捷高效地处理任何或小或大的项目。
Git 是 Linus Torvalds 为了帮助管理 Linux 内核开发而开发的一个开放源码的版本控制软件。
Git 与常用的版本控制工具 CVS, Subversion 等不同,它采用了分布式版本库的方式,不必服务器端软件支持。
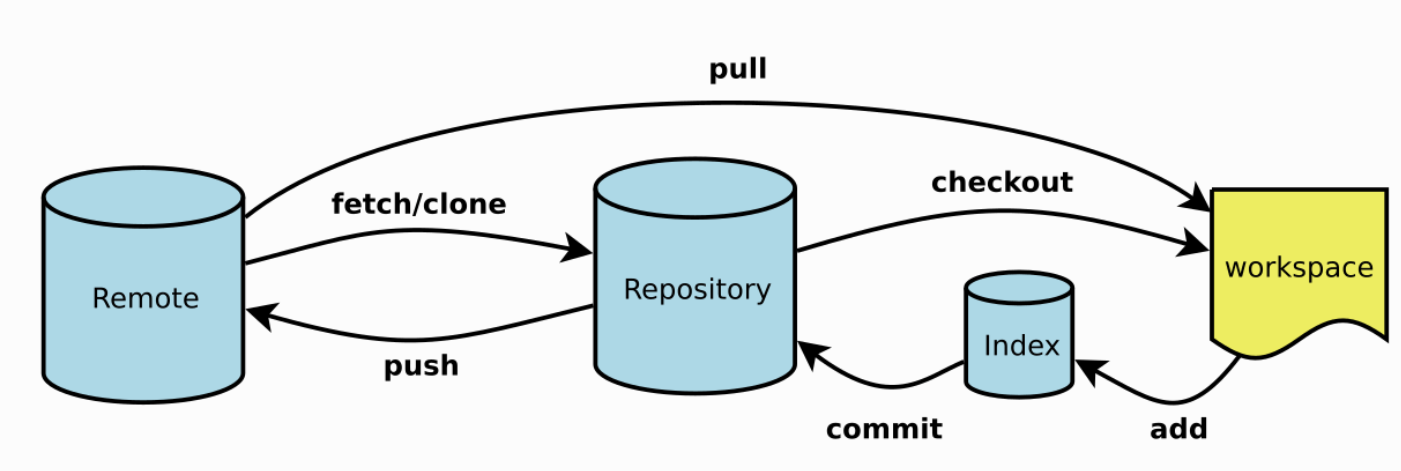
常用指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
|
$ git init # 在当前目录新建一个 Git 代码库
$ git clone [url] # 下载一个项目和它的整个代码历史
$ git config --list # 显示当前的 Git 配置
$ git config -e [--global] # 编辑 Git 配置文件
$ git add # 添加指定文件到暂存区
$ git rm # 删除工作区文件,并且将这次删除放入暂存区
$ git commit -m [message] # 提交暂存区到仓库区
$ git commit -a # 提交工作区自上次 commit 之后的变化,直接到仓库区
$ git commit --amend -m [message] # 使用一次新的 commit,替代上一次提交 如果代码没有任何新变化,则用来改写上一次 commit 的提交信息
$ git commit --amend [file1] [file2] ... # 重做上一次 commit,并包括指定文件的新变化
# 分支相关
$ git branch # 列出所有本地分支
$ git branch -r # 列出所有远程分支
$ git branch [branch-name] # 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支
$ git checkout [branch-name] # 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区
$ git checkout -b [branch] # 新建一个分支,并切换到该分支
$ git branch [branch] [commit] # 新建一个分支,指向指定 commit
$ git checkout -b [branch] [tag] # 新建一个分支,指向某个 tag
$ git branch --track [branch] [remote-branch] # 新建一个分支,与指定的远程分支建立追踪关系
$ git branch --set-upstream [branch] [remote-branch] # 建立追踪关系,在现有分支与指定的远程分支之间
$ git merge [branch] # 合并指定分支到当前分支
$ git cherry-pick [commit] # 选择一个 commit,合并进当前分支
$ git branch -d [branch-name] # 删除分支
$ git push origin --delete [branch-name] # 删除远程分支
$ git branch -dr [remote/branch] # 删除远程分支
# 标签
$ git tag # 列出所有 tag
$ git tag [tag] # 新建一个 tag 在当前 commit
$ git tag [tag] [commit] # 新建一个 tag 在指定 commit
$ git show [tag] # 查看 tag 信息
$ git push [remote] [tag] # 提交指定 tag
$ git push [remote] --tags # 提交所有 tag
# 查看
$ git status # 显示有变更的文件
$ git log # 显示当前分支的版本历史
$ git log --stat # 显示 commit 历史,以及每次 commit 发生变更的文件
$ git log --follow [file] # 显示某个文件的版本历史,包括文件改名
$ git log -p [file] # 显示指定文件相关的每一次 diff
$ git blame [file] # 显示指定文件是什么人在什么时间修改过
$ git diff # 显示暂存区和工作区的差异
$ git diff --cached [file] # 显示暂存区和上一个 commit 的差异
$ git diff HEAD # 显示工作区与当前分支最新 commit 之间的差异
$ git diff [first-branch]...[second-branch] # 显示两次提交之间的差异
$ git show [commit] # 显示某次提交的元数据和内容变化
$ git show --name-only [commit] # 显示某次提交发生变化的文件
$ git show [commit]:[filename] # 显示某次提交时,某个文件的内容
$ git reflog # 显示当前分支的最近几次提交
# 远程
$ git fetch [remote] # 下载远程仓库的所有变动
$ git remote -v # 显示所有远程仓库
$ git remote show [remote] # 显示某个远程仓库的信息
$ git remote add [shortname] [url] # 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名
$ git pull [remote] [branch] # 取回远程仓库的变化,并与本地分支合并
$ git push [remote] [branch] # 上传本地指定分支到远程仓库
$ git push [remote] --force # 强行推送当前分支到远程仓库,即使有冲突
$ git push [remote] --all # 推送所有分支到远程仓库
# 撤销
$ git checkout [file] # 恢复暂存区的指定文件到工作区
$ git checkout [commit] [file] # 恢复某个 commit 的指定文件到工作区
$ git checkout . # 恢复上一个 commit 的所有文件到工作区
$ git reset [file] # 重置暂存区的指定文件,与上一次 commit 保持一致,但工作区不变
$ git reset --hard # 重置暂存区与工作区,与上一次 commit 保持一致
$ git reset [commit] # 重置当前分支的指针为指定 commit,同时重置暂存区,但工作区不变
$ git reset --hard [commit] # 重置当前分支的 HEAD 为指定 commit,同时重置暂存区和工作区,与指定 commit 一致
$ git reset --keep [commit] # 重置当前 HEAD 为指定 commit,但保持暂存区和工作区不变
$ git revert [commit] # 新建一个 commit,用来撤销指定 commit,后者的所有变化都将被前者抵消,并且应用到当前分支
|
学习资源

